Multi-Party Computation for Secure, Private Data Collaboration
📷 https://rosemanlabs.com/en/blogs/getting-to-know-the-product
Introduction
In today’s digital age, data security and privacy have become paramount concerns for organizations across industries. The advent of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) offers a revolutionary approach to addressing these concerns, enabling secure and private data collaboration. In a recent interview with Toon Segers, co-founder of Roseman Labs, on the re:invent security podcast, we explored the intricacies of MPC and its transformative potential.
What is Multi-Party Computation (MPC)?
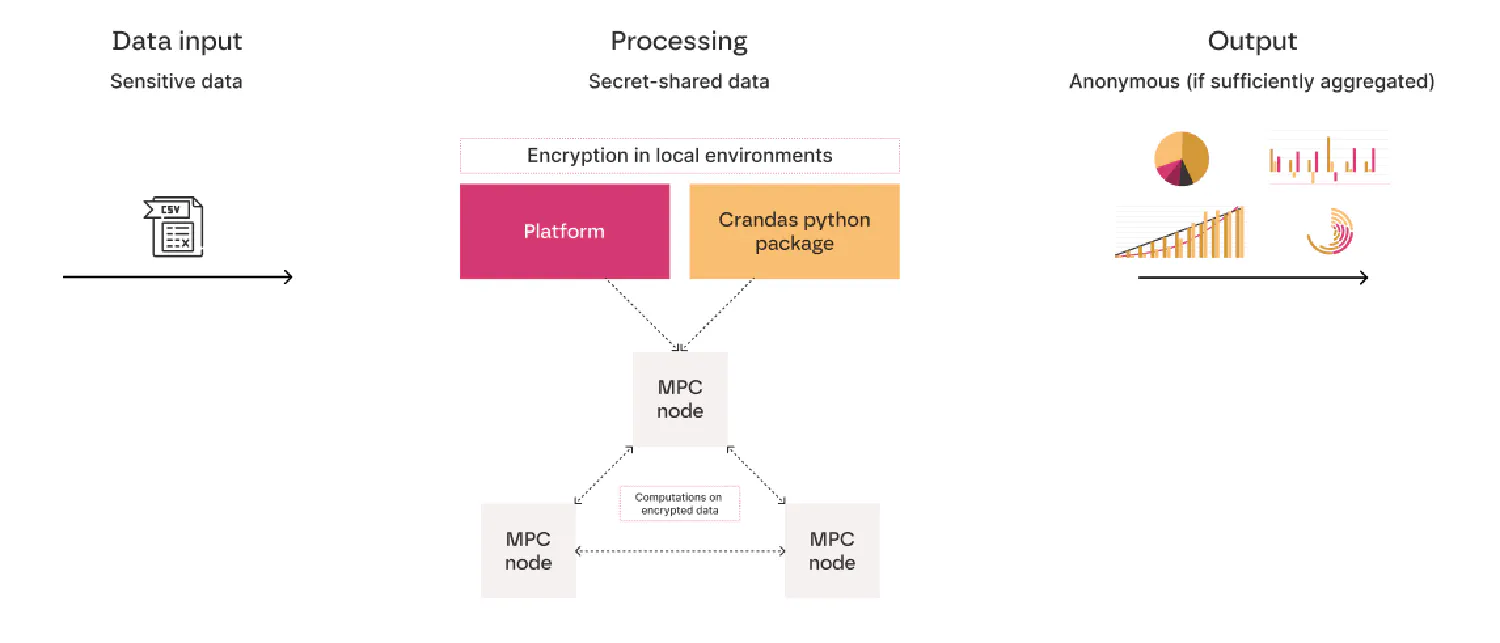
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is a solution that allows multiple parties to collaboratively compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. This means that each party’s data remains encrypted throughout the process, and only the final computation result is revealed. This technique ensures data privacy and security, making it possible to analyze and derive insights from sensitive data without exposing it to risks.
The Concept of MPC
At its core, MPC transforms the traditional approach to data analysis by eliminating the need for data to be decrypted at any stage. This is achieved through advanced cryptographic techniques that ensure each party’s input remains confidential. The computation process involves dividing the data into encrypted shares, which are then processed independently by each party. The final result is a combination of these encrypted shares, producing an output without ever exposing the individual data inputs.
Historical Context
The concept of MPC has its roots in the early 1980s, with seminal works by cryptographers such as Andrew Yao. Yao’s “Millionaires’ Problem” was one of the first formalizations of MPC, illustrating how two parties could determine who was wealthier without revealing their actual wealth. Since then, the field has evolved significantly, with modern MPC protocols capable of handling complex computations involving multiple parties.
Key Features and Benefits of MPC
-
Data Privacy and Confidentiality
MPC ensures that data remains encrypted from the moment it is inputted until the final computation result is outputted. This prevents unauthorized access and exposure of sensitive information during the analysis process. For example, in a healthcare setting, patient data can be analyzed to identify treatment patterns without revealing individual patient records.
-
Collaborative Analysis
MPC enables organizations to collaborate on data analysis without sharing the actual data. This is particularly useful in sectors like healthcare, finance, and cybersecurity, where data sensitivity is high. Financial institutions, for instance, can collaborate to detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns collectively, without exposing each other’s customer data.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
By maintaining data privacy, MPC helps organizations comply with stringent data protection regulations such as GDPR. It minimizes the risks associated with data sharing and enhances trust among collaborating parties. Organizations can confidently engage in data-driven projects knowing that their compliance with data protection laws is maintained.
-
Security Against Data Breaches
Since the data remains encrypted, MPC offers robust security against data breaches. Even if one party’s data center is compromised, the overall data privacy is maintained due to the distributed nature of the computation. This makes MPC an ideal solution for industries that handle highly sensitive information, such as government agencies and financial institutions.
Practical Applications of MPC
-
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare industry, MPC can be used to securely share and analyze patient data across different institutions. For example, hospitals can collaborate to analyze treatment outcomes without compromising patient privacy, leading to better healthcare solutions and patient care.
-
Financial Industry
Banks and financial institutions can utilize MPC to perform joint analyses on transaction data to detect fraudulent activities. By doing so, they can enhance their fraud detection mechanisms without revealing sensitive customer information to competitors.
-
Cybersecurity
Organizations can collaborate to identify and mitigate cyber threats by sharing threat intelligence securely using MPC. This collective approach strengthens overall cybersecurity postures without exposing proprietary or sensitive information.
Challenges and Considerations
While MPC offers significant advantages, its implementation comes with challenges:
-
Computational Overhead: MPC protocols can be resource-intensive, requiring substantial computational power, which may impact performance.
-
Complexity of Implementation: Developing and deploying MPC solutions requires specialized knowledge in cryptography and secure protocol design.
-
Scalability: Ensuring that MPC solutions scale effectively with the number of participants and the size of data sets is crucial for practical applications.
Addressing these challenges involves ongoing research and development to optimize MPC protocols for efficiency and scalability.
Conclusion
Multi-Party Computation represents a paradigm shift in how organizations approach data collaboration, offering a path to harness the power of collective data analysis without compromising privacy. As data privacy concerns continue to grow, MPC stands out as a promising solution for secure and private data collaboration across various industries.
For a more in-depth discussion on MPC, listen to our full interview with Toon Segers on the re:invent security podcast.
Note: This article is based on insights from the re:invent security podcast episode featuring Toon Segers, co-founder of Roseman Labs.
This article was originally published on LinkedIn: Multi-Party Computation for Secure, Private Data Collaboration.
